<Lab 12 문제 유형 요약>
- Program 1 : 파일 입력
- Program 2 : 파일 입력, 데이터 출력
- Program 3 : 파일 입력, 파일 같은지 비교하기
- Program 4 : 파일 입력, 파일 복사, 파일 생성, 파일 출력
- Program 5 : 파일 입력, 데이터 출력, 파일 생성, 파일 출력
- Program 6 : 파일 문자, 줄, 단어 수 세기
- Program 7 : 파일 크기 구하기
Program 1
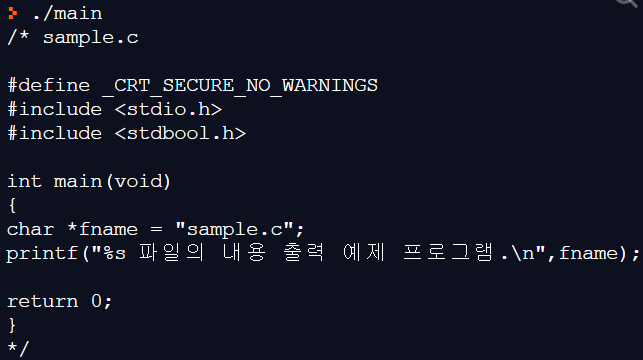
다음을 참고로 임의의 입력 텍스트 파일(예: sample.c)을 읽어 파일의 내용을 동일하게 출력하는 프로그램을 작성하시오.
- 입력 텍스트 파일은 임의의 .c 파일을 하나 선택한다.
- 함수 fgetc()/getc(), feof(), fprintf() 사용
|
/* sample.c #define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS #include <stdio.h> #include <stdbool.h>
int main(void) { char *fname = "sample.c"; printf("%s 파일의 내용 출력 예제 프로그램.\n",fname);
return 0; } */ |
#include <stdio.h>
int main()
{
char buffer[100];
FILE * fp = fopen("./sample.c","r");
if(fp==NULL) printf("file open error\n");
while(!feof(fp))
{
fgets(buffer,100,fp);
printf("%s",buffer);
}
printf("\n");
fclose(fp);
return 0;
}
Program 2
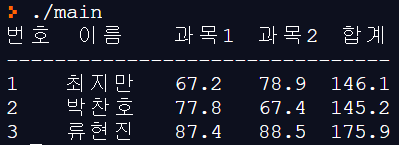
다음과 같은 입력 파일에서 그 내용을 읽어 각 학생의 점수의 합을 구하여 읽은 내용과 점수의 합을 함께 화면에 출력하는 프로그램을 작성하시오.
- 학생들의 정보를 담을 구조체를 정의하여 사용
- 입력 파일 : input.txt
| 1 최지만 67.2 78.9 2 박찬호 77.8 67.4 3 류현진 87.4 88.5 |
#include <stdio.h>
typedef struct _Person {
int num;
char name[10];
float sub1;
float sub2;
float sum;
} Person;
int main()
{
Person people[3];
char buffer[100];
FILE *fpr = fopen("input.txt", "r");
if (fpr == NULL) printf("file open error\n");
for(int i=0; i<3; i++)
{
fscanf(fpr," %s",buffer);
people[i].num = atoi(buffer);
fscanf(fpr," %s",buffer);
strcpy(people[i].name, buffer);
fscanf(fpr," %s",buffer);
people[i].sub1 = strtof(buffer, NULL);
fscanf(fpr," %s",buffer);
people[i].sub2 = strtof(buffer, NULL);
// 합계 계산
people[i].sum = people[i].sub1 + people[i].sub2;
}
fclose(fpr);
printf("번호 이름 과목1 과목2 합계\n");
printf("--------------------------------\n");
for (int i=0; i<3; i++)
{
printf("%d %6s %6.1f %6.1f %6.1f\n", people[i].num, people[i].name, people[i].sub1, people[i].sub2, people[i].sum);
}
return 0;
}
Program 3
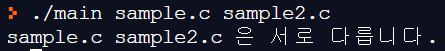
다음을 참고로 임의의 두 파일 내용이 정확히 일치하는지 검사하는 프로그램을 작성하시오.
- 비교를 위한 두개의 파일은 VisualStudio나 Dev C++ 에서 명령행 인자/실행 인자로 설정하여 프로그램을 실행하면 된다.

#include <stdio.h>
int main(int argc, char *fname[])
{
char *file1 = fname[1], *file2 = fname[2];
FILE *fp1 = fopen(file1, "r");
FILE *fp2 = fopen(file2, "r");
if (fp1 == NULL || fp2 == NULL) printf("내용을 비교할 파일 2개가 필요합니다.");
while (1)
{
int char1 = fgetc(fp1);
int char2 = fgetc(fp2);
if (char1 == EOF && char2 == EOF) break;
if (char1 != char2)
{
printf("%s %s 은 서로 다릅니다.\n",fname[1], fname[2]);
fclose(fp1);
fclose(fp2);
return 0;
}
}
printf("두 파일은 서로 같습니다.\n");
fclose(fp1);
fclose(fp2);
return 0;
}
Program 4
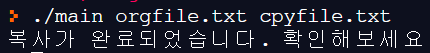
다음을 참고로 파일을 복사하는 mycopy 프로그램을 작성하시오.
- 명령어 mycopy로 명령행 인자인 srcfile을 dstfile로 복사하는 프로그램
- cmd 윈도우에서 실행하는 경우 C:\> mycopy srcfile dstfile
- IDE에서 인자 설정으로 실행도 가능
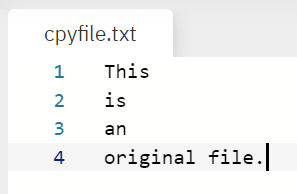
| This is an original file. |
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
int main(int argc, char *fname[])
{
int cnt;
char buffer[10] = { 0, };
FILE *src = fopen(fname[1], "r");
FILE *dst = fopen(fname[2], "w");
if (src==NULL) printf("원본파일이 열리지 않습니다.");
if (src == NULL && dst == NULL) printf("복사할 원본 파일과 대상 파일이 없습니다.");
while (!feof(src))
{
cnt = fread(buffer, sizeof(char), 9, src);
fwrite(buffer, sizeof(char), cnt, dst);
memset(buffer, 0, 5);
}
printf("복사가 완료되었습니다. 확인해보세요.\n");
fclose(dst);
fclose(src);
return 0;
}
Program 5
다음을 참고로 파일 내부의 문자를 대문자는 소문자로, 소문자는 대문자로 변환하여 출력하고, 변경된 내용을 파일로도 저장하는 프로그램을 작성하시오.
- isalpha(), isupper(), tolower(), toupper(), rewind() 함수등 사용하면 편리
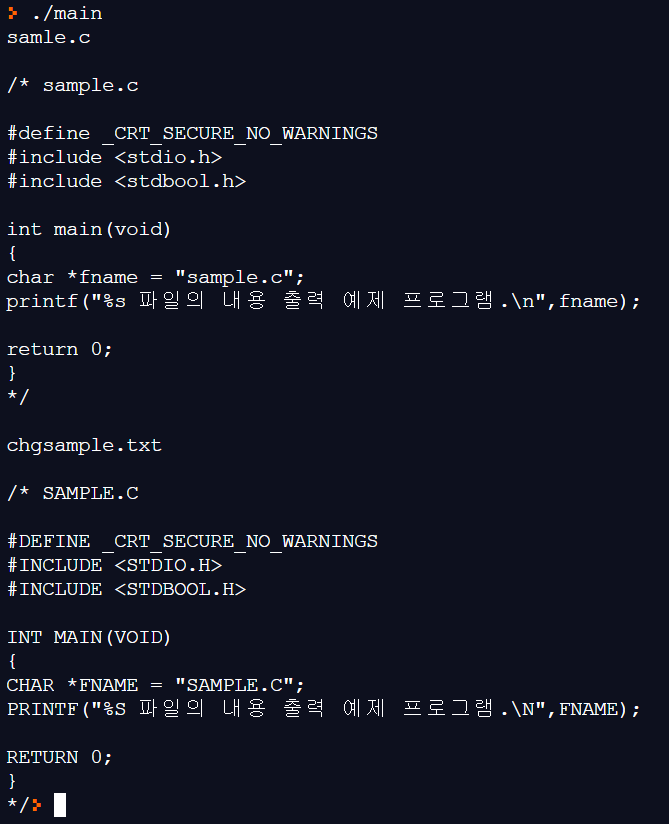
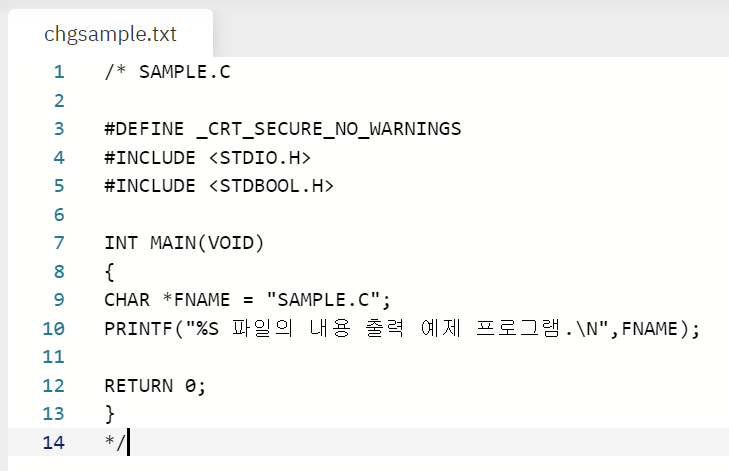
- 원본 파일과 변경 파일이 각각 sample.c 와 chgsampl.c 인 경우
#include <stdio.h>
int main()
{
char buffer[100];
int line = 0;
FILE *fpr = fopen("sample.c", "r");
FILE *fpw = fopen("chgsample.txt", "w");
if (fpr == NULL) printf("file open error\n");
printf("samle.c\n\n");
while (!feof(fpr))
{
fgets(buffer, 300, fpr);
printf("%s", buffer);
for (int i=0; buffer[i]; i++)
{
if (islower(buffer[i])) buffer[i] = toupper(buffer[i]);
}
fputs(buffer, fpw);
}
printf("\n\n");
fclose(fpr);
fclose(fpw);
fpr = fopen("chgsample.txt", "r");
printf("chgsample.txt\n\n");
while (!feof(fpr))
{
fgets(buffer, 300, fpr);
printf("%s", buffer);
}
fclose(fpr);
return 0;
}
Program 6
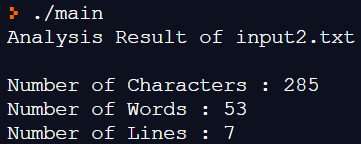
다음을 참고로 파일 내부에 있는 문자 수, 단어 수, 라인 수를 출력하는 프로그램을 작성하시오.
- 문자는 영어 알파벳을 의미하고, 단어는 공백 문자, ‘\n’, !, ?,(,) 등으로 구분되는 단어로 한다. strtok() 사용하여 단어 구분
- 문자는 알파벳만 포함한 경우, 단어는 숫자 포함
- input2.txt
| C is a general purpose, procedural computer programming language supporting structured programming, and recursion. C was originally developed at Bell Labs by Dennis Ritchie. C has been standardized by the ANSI since 1989 and by the International Organization for Standardization(ISO). As of September 2020, C is the most popular programming language. |
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <ctype.h>
int main()
{
char buffer[100];
int character = 0, word = 0, line = 0;
FILE* fp = fopen("input2.txt", "r");
if (fp == NULL) printf("file open error\n");
printf("Analysis Result of input2.txt\n\n");
while (!feof(fp))
{
fgets(buffer, 300, fp);
for (int i = 0; buffer[i]; i++)
{
if (isalpha(buffer[i])) character++;
}
char* piece = strtok(buffer, " .,()\r\n\t'");
while (piece)
{
word++;
piece = strtok(NULL, " .,()\r\n\t");
}
line++;
}
printf("Number of Characters : %d\n", character);
printf("Number of Words : %d\n", word);
printf("Number of Lines : %d\n", line);
fclose(fp);
return 0;
}
Program 7
다음을 참고로 파일의 크기를 출력하는 프로그램을 작성하시오.
- 함수 fseek()과 ftell()을 이용하면 쉽게 구할 수 있음
- 명령행 인자(main 함수 인자)로 input2.txt 사용한 출력 결과

#include <stdio.h>
int main()
{
int size;
FILE *fp = fopen("input2.txt", "r");
fseek(fp, 0, SEEK_END);
size = ftell(fp);
printf("input2.txt 파일 크기 :%d 바이트\n", size);
fclose(fp);
return 0;
}

'College Computer Science > C Language' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [C 프로그래밍 실습] 동적 메모리와 전처리 1 (Lab 13) (0) | 2021.01.08 |
|---|---|
| [C 프로그래밍 실습] Report 04 (0) | 2021.01.08 |
| [C 프로그래밍 실습] 함수와 포인터 활용 2 (Lab 11) (0) | 2021.01.07 |
| [C 프로그래밍 실습] 3인 블랙잭 Blackjack 카드 게임 만들기 (Term Project) (1) | 2021.01.07 |
| [C 프로그래밍 실습] 함수와 포인터 활용 1 (Lab 10) (0) | 2021.01.06 |




댓글